Accurate, Large Minibatch SGD
Training ImageNet in 1 Hour
Main Idea
- Higher training speed requires larger mini-batch size.
8192 images one batch, 256 GPUs
- Larger mini-batch size leads to lower accuracy
- Linear scaling rule for adjusting learning rates as a function of minibatch size
- Warmup scheme overcomes optimization challenges early in training
Background
- mini-batch SGD
- Larger mini-batch size lead to lower accuracy.
mini-batch SGD

mini-batch SGD
- Iteration(in FaceBook Paper):
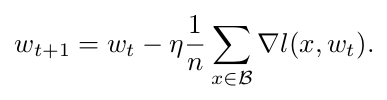
Convergence:
- Learning Rate:
- Converge Speed:
M: batch size, K: iteration number, σ²: stochastic gradient variance
- Learning Rate:
Goal
- Use large minibatches
- scale to multiple workers
- Maintaining training and generalization accuracy
Solution
- Linear Scaling Rule: When the minibatch size is multiplied by k, multiply the learning rate by k.
Analysis
- k iteration, minibatch size of n:
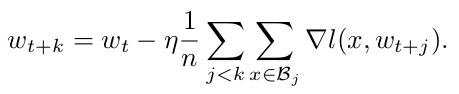
- 1 iteration, minibatch size of kn:
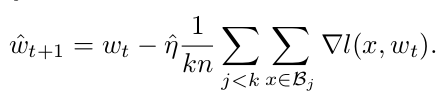
- Assume gradients of the above fomulas are equal
- Two updates can be similar only if we set the second learning rate to k times the first learning rate.
Conditions that assumption not hold
- Initial training epochs when the network is changing rapidly.
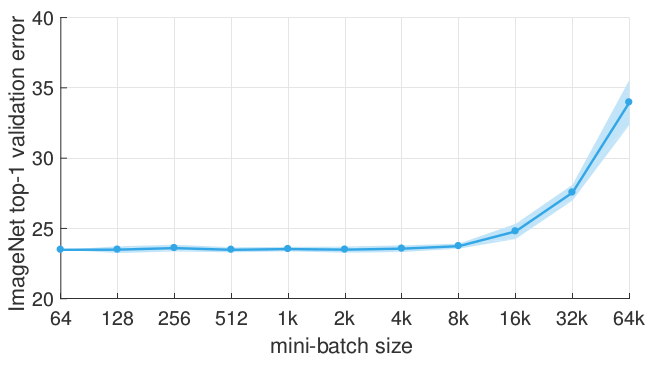
- Results are stable for a large range of sizes, beyond a certain point
Warm Up
- Low learning rate to solve rapid change of the initial network.
- Constant Warmup: Sudden change of learning rate causes the training error to spike.
- Gradual warmup: Ramping up the learning rate from a small to a large value.
- start from a learning rate of η and increment it by a constant amount at each iteration such that it reaches η̂ = kη after 5 epochs.